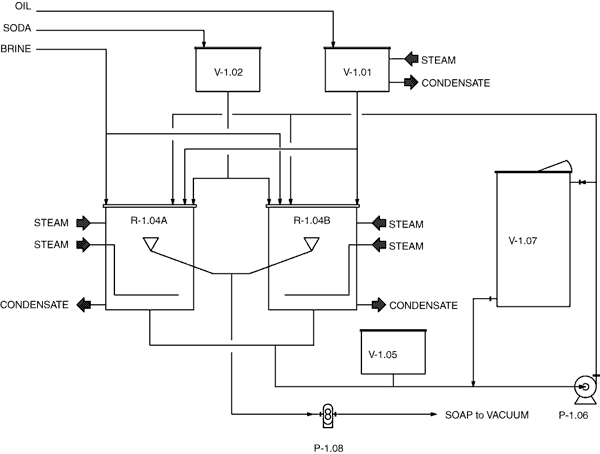
Oils, caustic
soda and water are fed into the pan equipped with direct steam
heating system. Steam is fed in order to bring the content to
the boiling temperature and to facilitate the mixing action required
to start the saponification reaction.
When the reaction
starts, as saponification is an exothermic reaction, steam feeding
can be reduced or completely eliminated.
When the saponification
is completed, brine is added into the pan to separate the content
into two phases: an upper phase containing soap, and a lower
phase containing salt, caustic soda, impurities and glycerine.
The lower phase is discharged into a vessel and can be sent to
a glycerine recovery plant.
After further
washing by dilution with water and separation with brine, the
soap is drawn out of the pan and is pumped to a Vacuum Cooling
and Drying Plant.